Why fear is not a fundamentally negative emotion
 Fear describes the feeling of being “exposed” as well as “uncanniness”. Although in most cases the feeling of fear is perceived as unpleasant, if not threatening, the feeling itself is also extremely useful: without fears our ancestors would hardly have been able to survive. And even in modern times, fear warns our brain of countless dangers. Fast approaching cars, abandoned parking garages at night, narrow dark alleys, angry faces and much more we unconsciously perceive as a threat. Our brain, especially a part of it: our limbic brain warns us at lightning speed, even before we cognitively grasp the situation. Our “feeling brain” is significantly faster than our “thinking brain”. But anxiety can also have its cause in a mental disorder and thus be of a pathological nature .
Fear describes the feeling of being “exposed” as well as “uncanniness”. Although in most cases the feeling of fear is perceived as unpleasant, if not threatening, the feeling itself is also extremely useful: without fears our ancestors would hardly have been able to survive. And even in modern times, fear warns our brain of countless dangers. Fast approaching cars, abandoned parking garages at night, narrow dark alleys, angry faces and much more we unconsciously perceive as a threat. Our brain, especially a part of it: our limbic brain warns us at lightning speed, even before we cognitively grasp the situation. Our “feeling brain” is significantly faster than our “thinking brain”. But anxiety can also have its cause in a mental disorder and thus be of a pathological nature .
What is meant by fear?
The term “anxiety” comes from the Latin verb ” angere ” and the Greek “agchein”, which translated into German means “to close the throat” or “ to choke “. Internationally, this German word has become common in the context of existential philosophy and psychoanalysis. Unlike fear, which is clearly focused on an external danger, anxiety is considered indeterminate. It usually comes over people uncontrollably and involuntarily.
In the field of psychology, a distinction is made here between a trait and a state: in the first form, this occurs in situations that are classified as dangerous, although there is no acute threat. State anxiety, on the other hand, represents a temporary emotion due to an actual danger.
Anxiety comes in many forms. For example as
- Fear of high altitude
- Fear of spiders
- Fear of snakes
- Fear of confined spaces
- Fear of exams
- Fear of flying
- Fear of the dentist
- Fear of making a grand entrance or even panic about blushing.
How does fear affect our health and well-being?
As mentioned at the beginning, fear per se is not a bad advisor, but fulfills a vital function as a primal human emotion. Because it is this basic emotion that allows us to recognize danger and react accordingly. It reminds us to be more attentive and careful. Well-founded fears provide us with the necessary energies to mobilize our forces, accept challenges, take protective measures and act decisively. In many cases, this is what makes top performance possible in the first place. Already our ancestors reacted thanks to this archaic emotion depending on the threat with attack or flight. Accordingly, object-related anxiety, for example, is not exclusively a paralyzing emotion, but also a mobilizing one.
Produced and controlled is this emotion with its associated body signals in the amygdala, which is considered in the brain to be the center of anxiety- and fear-guiding behavioral assessment. Together with the hippocampus, the amygdala also has another important function; namely, building emotional memory, also called body memory. Here, the somatic markers play an important role. People have different anxiety behaviors, which can lead to anything from a queasy feeling to significant outbursts of anxiety along with distressing physical sensations.
However, in the case of a recurrent, exaggerated and unfounded fear reaction, the boundary between non-disease and pathological fear may be crossed.
Learn more about fear

Anxiety: causes and development of anxiety
How do anxiety reactions arise and what are the triggers? Can a butterfly cause fear in us? Most of us would say no. And yet, smaller insects manage to frighten
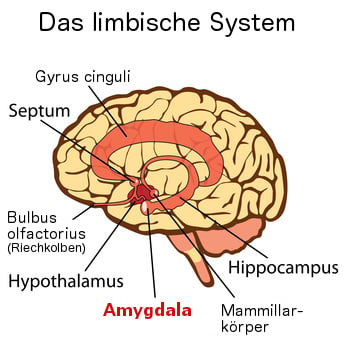
Fear: How the amygdala controls our fears
What processes in the brain trigger the fear Quite a few people harbor fear of certain situations. Although a fear reaction can have different causes, the different fears have one

Anxiety: causes and development of anxiety
How do anxiety reactions arise and what are the triggers? Can a butterfly cause fear in us? Most of us would say no. And yet, smaller insects manage to frighten

Fear: How the amygdala controls our fears
What processes in the brain trigger the fear Quite a few people harbor fear of certain situations. Although a fear reaction can have different causes, the different fears have one